ASTALAVISTA! Why Do We Need Buffer Solution
In fact we do not even need to exhaust all of the acid or base in a buffer to overwhelm it. The blank allows you to set the spectrophotometer to zero before you measure your unknown solution.
Chemistry Of Buffers And Buffers In Our Blood Article Khan Academy
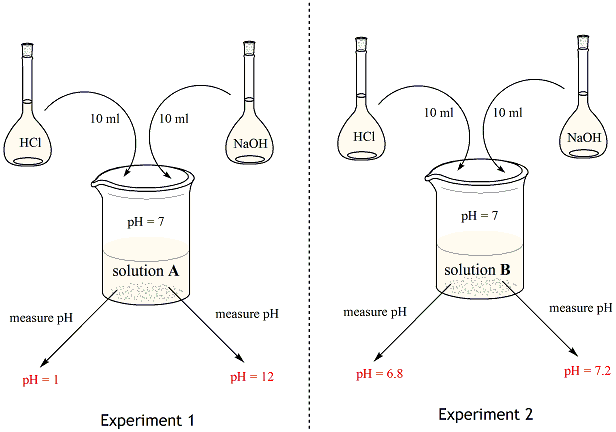
Buffer solutions are used as a means of keeping pH at a nearly constant value in a wide variety of chemical applications.

Why do we need buffer solution. Most biochemical reactions that are essential for life only take place in a narrow pH range. So you use solutions of known pH and adjust the meter to display those values. Its buffering action will diminish rapidly as a given component nears depletion.
Calculation of the pH of a Buffer Solution. The indicator color methyl orange shows that a small amount of acid added to a buffered solution of pH 8 beaker on the left has little affect on the buffered. Buffer solutions are used to calibrate pH meters because they resist changes in pH.
Acetate buffers are used in biochemical studies of enzymes and other chemical components of cells to prevent pH changes that might change the biochemical activity of these compounds. Calculate the pH of an acetate buffer that is a mixture with 010 M acetic acid and 010 M sodium acetate. Also for EDTA pKa4 1026.
Ad Search Graingers Online Catalog. When you use a pH meter to measure pH you want to be sure that if the meter says pH 700 the pH really is 700. Phosphate-buffered saline or PBS is isotonic to human body fluids.
For example say you lysed some cell. The presence of buffers ensures that the bodys pH remains in this range despite changes in the surroundings. Buffers are an important part of the biochemical processes of living things because they help keep the pH within organisms body stable.
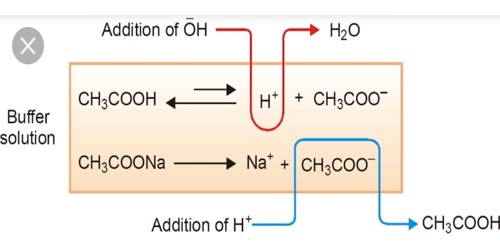
A buffer is a solution that can resist pH change upon the addition of an acidic or basic components. The balanced equation for this reaction is. It is able to neutralize small amounts of added acid or base thus maintaining the pH of the solution relatively stable.
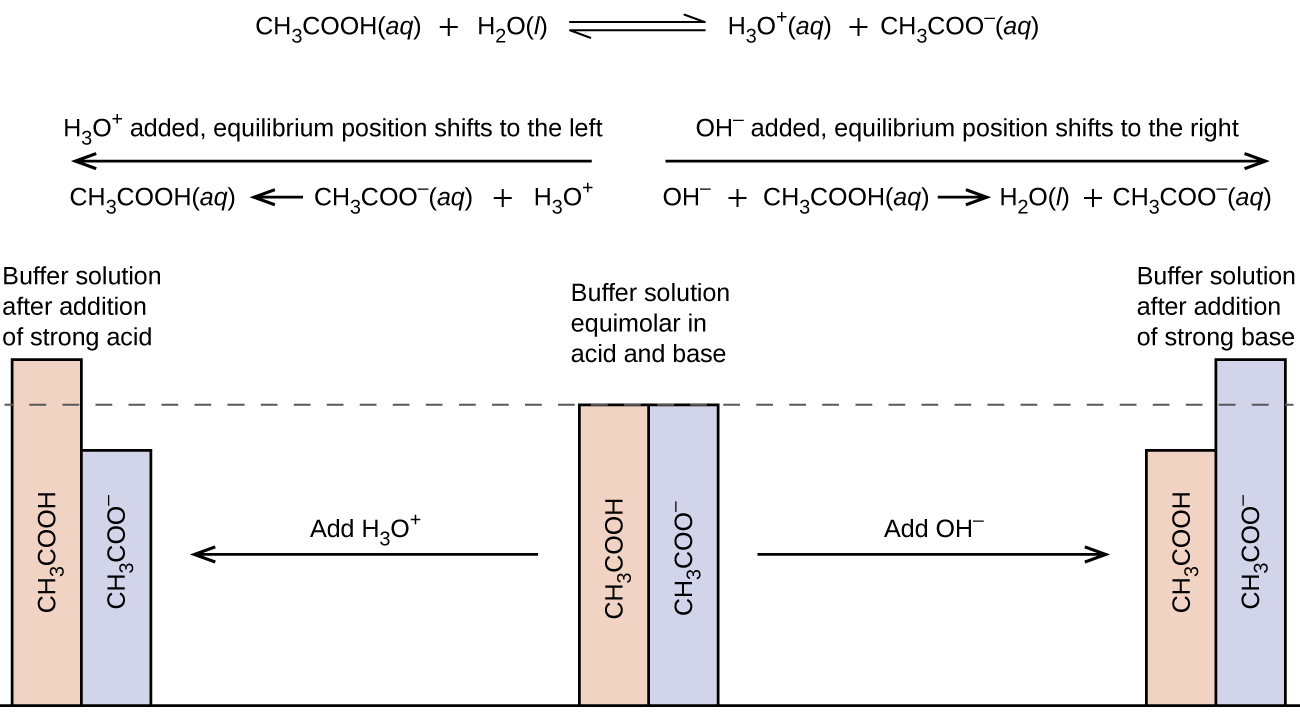
When an acid H or H 3 O is added to the solution the equilibrium moves to the left as there are hydrogen ions. A buffer is a solution that can resist pH change upon the addition of an acidic or basic components. The components act in such a way that addition of an acid or base results in the formulation of a.
The blank solution will contain everything that the unknown solution the one you want to measure except for the think you wish to measure. For example suppose we want to make a buffer based on acetic acid. Buffer solutions resist changes in pH and so lets think about a solution of a weak acid and its conjugate base so here we have H a which is our generic weak acid and so the conjugate base would be a minus and a buffer solution needs to have substantial amounts of both present and thats what Im trying to represent over here so we have a beaker that has in this case equal amounts of H a and a minus and.
The option b is false. If the pH of blood falls below 74 buffers act to take up hydrogen atoms and decrease the acidity of the blood 1 3. This is important for processes andor reactions which require specific and stable pH ranges.
HA H 2 O. The pH of buffer solution does not change on standing for long. For example blood in the human body is a buffer solution.
This moves the position of equilibrium to the right and favours formation of the complex Le Châteliers Principle. Eugenio Marongiu Getty Images. Calculation of the Buffer Capacity.
It is able to neutralize small amounts of added acid or base thus maintaining the pH of the solution relatively stable. This is important for processes andor reactions which require specific and stable pH ranges. Calculation of the pH of a Buffer Solution after Addition of a Small Amount of Strong Base.
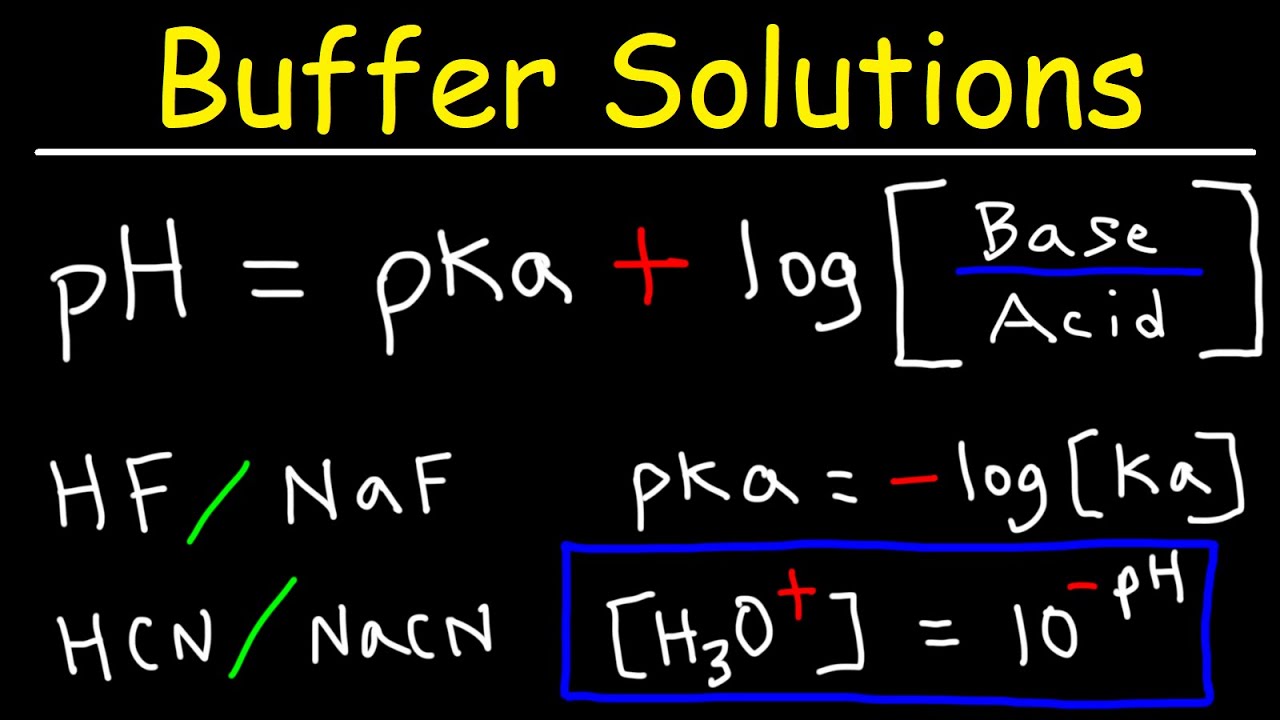
In order to calculate the pH of the buffer solution you need to know the amount of acid and the amount of the conjugate base combined to make the solution. Buffers working in the body fluid adjust the pH level of the blood and function to lower pH if its level rises above 74 by making the blood slightly more acidic 1 3. This is important for processes andor reactions which require specific and stable pH ranges.
A buffer is a solution that can resist pH change upon the addition of an acidic or basic components. Buffer solutions are resistant to pH change because of the presence of an equilibrium between the acid HA and its conjugate base A. The pH of a buffer solution changes slightly on the addition of a small amount of acid or base.
It is able to neutralize small amounts of added acid or base thus maintaining the pH of the solution relatively stable. Buffer solutions have a definite pH. Buffers are compounds that resist changes in pH upon the addition of limited amounts of acids or bases.
Updated 10 months ago Author has 83K answers and 54M answer views. The pH of a buffer solution does not change on dilution. Because one of the pair is going to be an ion and you cant have an ion without a counterion.
H 3 O A. Buffer systems are usually composed of a weak acid or base and its conjugate salt. PBS or phosphate-buffered saline is a buffer solution that is particularly valuable because it mimic the ion concentration osmolarity and pH of human body fluids.
Buffer solutions do not have a definite pH. A buffer would have pHpKa1 or pKa-1. To make a good buffer a buffer that can retain pH well we need to know the pKa of the acid or pKb for base.
Carrying out the reaction in a basic buffer solution removes the H as it is formed. How to Prepare Phosphate-Buffered Saline Solution. In a buffer solution there is an equilibrium between a weak acid HA and its conjugate base A or vice versa as stated above.

Buffer Solution Ph Computer Simulation Buffer Solution Computer Simulation Solutions

General Chemistry Notes Full Course Pdf Notes Chemistrynotes Com Chemistry Notes Chemistry Chemistry Lessons
Buffer Solution Assignment Point

49 Buffer Solution Ph Calculations Buffer Solutions Buffers Titrations And Solubility Equilibria Chemis Buffer Solution Chemistry Classroom Chemistry

Buffer Solutions Video Khan Academy

Buffer Solutions Biochemistry The Biology Notes

What Is A Biological Buffer And How To Choose The Best Buffer For Your Experiment Goldbio

Buffer Solution Its Characteristics Types And Preparations

Buffer Solutions Definition Types Preparation Examples And Videos

Buffer Buffering Capacity Properties Of Good Buffer And Role Of Buffer In Vitro And In Vivo Online Biology Notes

How To Calculate The Ph Of A Buffer Solution After Adding Acid Hcl Youtube



Comments
Post a Comment